
The energy density of a fuel per unit mass is called the specific energy of that fuel. If sacrificing the range is undesirable, it becomes necessary to carry that much more fuel. The same mass of lithium-ion storage, for example, would result in a car with only 2% the range of its gasoline counterpart. Given the high energy density of gasoline, the exploration of alternative media to store the energy of powering a car, such as hydrogen or battery, is strongly limited by the energy density of the alternative medium. The higher the energy density of the fuel, the more energy may be stored or transported for the same amount of volume. In energy storage applications the energy density relates the energy in an energy store to the volume of the storage facility, e.g.
In energy storage and fuels Selected energy densities plot The lower value (LHV), or net heat of combustion, does not include the heat which could be released by condensing water vapor, and may not include the heat released on cooling all the way down to room temperature.Ī convenient table of HHV and LHV of some fuels can be found in the references.The higher value (HHV), or gross heat of combustion, includes all the heat released as the products cool to room temperature and whatever water vapor is present condenses.There are two kinds of heat of combustion: But as a source of heat or for use in a heat engine, the relevant quantity is the change in standard enthalpy or the heat of combustion.

#Joules from fusion vs fission free
This is given by the change in standard Gibbs free energy. Another is the theoretical amount of electrical energy that can be derived from reactants that are at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. One is the theoretical total amount of thermodynamic work that can be derived from a system, at a given temperature and pressure imposed by the surroundings. There are several different types of energy content. Electrochemical reactions are used by most mobile devices such as laptop computers and mobile phones to release energy from batteries. Liquid hydrocarbons (fuels such as gasoline, diesel and kerosene) are today the densest way known to economically store and transport chemical energy at a large scale (1 kg of diesel fuel burns with the oxygen contained in ≈15 kg of air). Chemical reactions are used by organisms to derive energy from food and by automobiles to derive energy from gasoline. Nuclear reactions take place in stars and nuclear power plants, both of which derive energy from the binding energy of nuclei. In order of the typical magnitude of the energy released, these types of reactions are: nuclear, chemical, electrochemical, and electrical.

There are different types of energy stored in materials, and it takes a particular type of reaction to release each type of energy. A pressure gradient describes the potential to perform work on the surroundings by converting internal energy to work until equilibrium is reached. Likewise, the energy required to compress a gas to a certain volume may be determined by multiplying the difference between the gas pressure and the external pressure by the change in volume. For example, the energy density of a magnetic field may be expressed as and behaves like a physical pressure. In cosmological and other general relativistic contexts, however, the energy densities considered are those that correspond to the elements of the stress-energy tensor and therefore do include mass energy as well as energy densities associated with pressure.Įnergy per unit volume has the same physical units as pressure and in many situations is synonymous. Often only the useful or extractable energy is measured, which is to say that inaccessible energy (such as rest mass energy) is ignored.
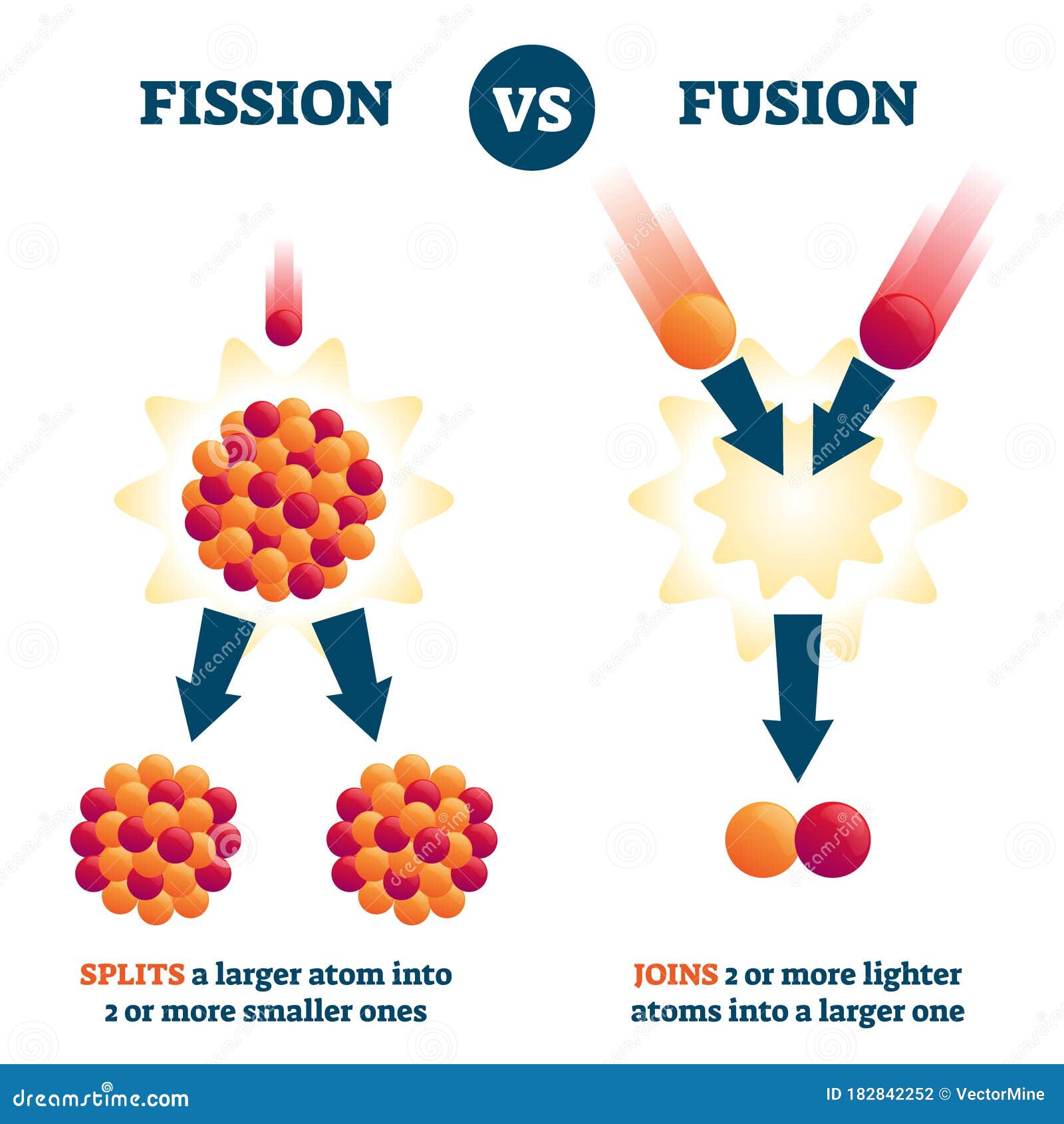
It is sometimes confused with energy per unit mass which is properly called specific energy or gravimetric energy density. In physics, energy density is the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
